- Markforged Onyx Filament Review & Alternatives [2024] - December 11, 2024
- 17 Best Professional 3D Printers: Commercial, Desktop, & Industrial [2024] - December 10, 2024
- Best 3D Printers (Industrial, Desktop, & More) [2024 Guide] - July 20, 2024
3D printing is an increasingly popular technology for prototyping and manufacturing various objects and products, but it can also be a major contributor to sustainability. By reducing waste, eliminating the need for costly molds and tooling, and enabling on-demand production, 3D printing is becoming a vital part of green initiatives and helping to create a more sustainable future.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, 3D printing has the potential to reduce waste and materials costs by almost 90% (compared to traditional manufacturing) while also cutting manufacturing energy use in half.
This post will explore how 3D printing can revolutionize production methods, create sustainable products, and significantly reduce the environmental impact associated with traditional manufacturing processes.
What is Considered Sustainable 3D Printing?
Sustainable 3D printing leverages the power of 3D printing technology to minimize waste, conserve resources, and mitigate the environmental impact commonly associated with traditional manufacturing methods. It encompasses a range of practices and strategies that promote sustainability throughout the entire 3D printing lifecycle, from material selection and energy efficiency to end-of-life management.
- Material selection: This involves selecting eco-friendly and biodegradable 3D printing materials with a reduced carbon footprint, such as PLA (polylactic acid), PA11, and BioPETG.
- Energy Efficiency: Involves using energy-efficient printers such as Nexa3D SLS 3D printers, optimizing print settings to reduce power consumption, and exploring alternative energy sources
- End-of-life Management: This includes properly recycling or reusing excess or failed prints, as well as considering the recyclability or biodegradability of materials used. By ensuring that materials are disposed of or recycled in an environmentally responsible manner, professionals can close the loop and contribute to a circular economy. In a circular economy, the emphasis is on keeping products, materials, and resources in continuous use for as long as possible through strategies such as reuse, repair, remanufacturing, and recycling.
Examples of Sustainable 3D Printing

JawsTec saved over 2 tons of recycled powder while doubling its production output
About JawsTec
JawsTec is a manufacturing service provider that specializes in 3D printing, CNC machining, and metal fabrication production services across several industries. They are dedicated to providing innovators, engineers, and entrepreneurs access to rapid prototyping while utilizing high-volume production to produce parts for several large businesses, including notable names like Tesla, Apple, BMW, Ford, and SpaceX.
The challenge JawsTec experienced
JawsTec was wasting over two tons of powder each year and had to forgo usage of 30% of their thermoplastic powder, while also bearing the cost of its storage and disposal per regulations.
This waste raised the company’s operating overhead and impacted profits. It also represented a significant environmental issue for a company committed to sustainable manufacturing. “Our older systems were running a 50% new powder refresh rate, which is not sustainable,” noted JawsTec CEO Oscar Klassen.
JawsTec was looking to raise their additive manufacturing output, streamline costs, and enhance company sustainability by significantly lowering the waste ratio of sintering powders used.
The Solution
To eliminate powder waste and increase machine throughput and uptime, JawsTec chose the QLS selective laser sintering technology by Nexa3D.
With assistance from Nexa3D’s application engineering team, JawsTec swiftly implemented four QLS 230 printers and a QLS 820 printer, completing installation and training within a month. Upon becoming operational and integrated into their production process, JawsTec promptly started utilizing a blend of new sintering powder and recycled powder sourced from their legacy SLS and MJF platforms. By leveraging the high packing density rate of the QLS series printers, JawsTec now maximizes the usage of their powders, achieving a utilization rate of 100% and optimizing the consumption of recycled powder.
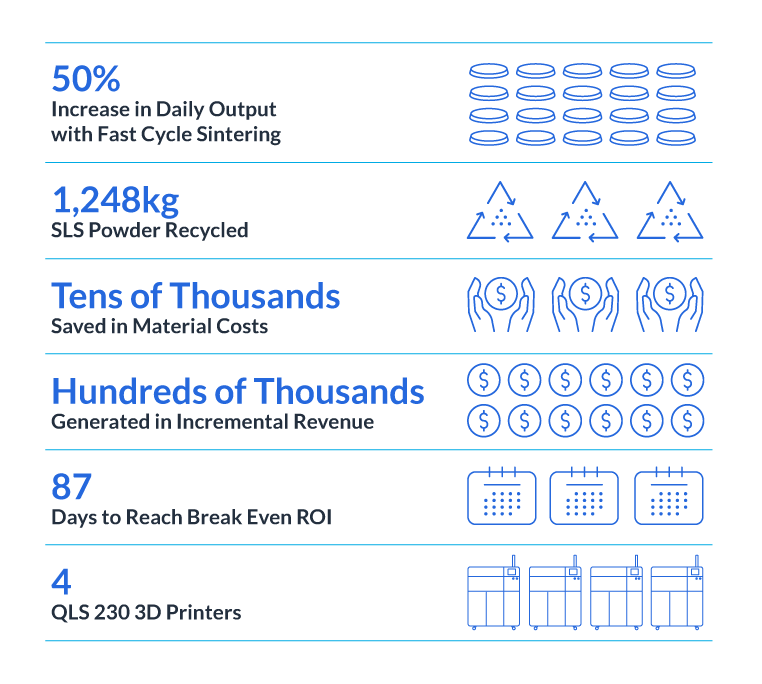
JawsTec achievements with Nexa3D QLS 230 and 820
“The QLS 230 printers give us the ability to use end-of-life powder from other SLS and MJF machines to produce high-quality parts while eliminating powder waste. On top of the operational sustainability, the smaller build volume of the QLS 230 allows for a much shorter build cycle and cooling cycle with zero negative effect on part accuracy or surface quality.”
Oscar Klassen,
Co-Founder & CEO, JawsTec
How 3D Printing Can Reduce Waste
Using Additive instead of Subtractive Manufacturing Practices
Traditional subtractive manufacturing practices involve drilling, cutting, sawing, and shaping materials to create structures. These processes involve removing parts of various raw materials to generate the necessary dimensions for the final product. As a result, many of these subtractive manufacturing processes lead to material waste that is often non-recyclable.
In contrast, the additive nature of 3D printing means finished parts are made layer by layer–utilizing a variety of techniques and processes depending on the specific 3D printing technology employed. Commonly used techniques include fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), digital light processing (DLP), etc.
Regardless of the specific technique, the additive nature of 3D printing allows for precise control over the construction of the object, as each layer is added sequentially. This eliminates or drastically reduces waste since structures are created only using the necessary amount of raw materials.
Improved Production Efficiency
Improved production efficiency involves streamlining processes, eliminating bottlenecks, and maximizing output–all while minimizing costs and resource consumption.
For example, 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, which is a process of quickly creating physical prototypes or models of a design. It allows designers and engineers to iterate and refine their designs at a much faster pace compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
With 3D printing, designers can turn their digital designs into physical objects in a matter of hours or days, depending on the complexity and size of the prototype. This accelerated timeline enables faster feedback loops, as designers can test and evaluate their prototypes, identify potential design flaws or improvements, and make necessary adjustments before moving forward with production.
On-demand Manufacturing
It’s not uncommon for manufacturers to have a large number of products in inventory, even if they don’t have guaranteed demand.
With on-demand manufacturing, companies can utilize 3D printing technology to produce customized products or parts as needed, in response to customer orders or demand signals. For example, R3D–an engineering and 3D printing service provider–had only three months to turn around 7200 custom parts or 400 police cars for the French Gendarmerie. Luckily, with the use of Nexa3D’s NXE 400 3D printer, R3D was able to achieve the initial run of components well within the 3-month timeline.
Not only were the components completed, but the reception was so positive that two additional orders for 12,600 parts for 700 additional vehicles were placed and delivered. In one year, R3D used their single NXE 400 3D printer to manufacture 18,000 parts for 1,000 police cars.
On-demand manufacturing eliminates the need for large-scale production and storage of inventory, which requires time, energy, and financial resources. It ensures that items are created only when needed, reducing waste associated with surplus or obsolete inventory.
Local Production For Reduced Carbon Emissions
Transportation is one of the largest sources of greenhouse gas emissions in the United States.
With 3D printing, printers can be installed in workplaces for small and large-scale production to facilitate the creation of parts, prototypes, and items locally rather than having them shipped from far away.
This localized approach reduces the need for long-distance shipping and associated packaging, leading to a reduction in transportation-related waste and carbon emissions.
Material Recyclability
Material recyclability in 3D printing reduces waste by enabling the reuse of excess or failed prints, as well as support structures and discarded prototypes. These materials are processed and transformed back into usable filaments or resins, thereby reducing the need for new material inputs.
Next we’ll take a look at a few ways to improve recycling within 3D printing.
How to Recycle 3D Printer Waste
While recycling 3D printer waste might have been difficult in the past, the advent of technology has made it possible to reduce and reuse waste.
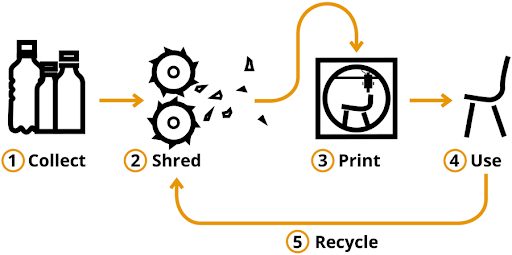
The recycling process is different for various 3D printer materials. Plastic products, especially those made from PLA, are more commonly recycled than their metal and resin counterparts. PLA is thermoplastic and can be melted and resolidified without changing its chemical composition. It is also made from renewable resources, such as corn starch or sugarcane. This means that it is a sustainable material that can be recycled without contributing to the production of more plastic waste.
Other materials that can be recycled include PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol), ABS, most nylons, TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane), most resins, and metal powders such as stainless steel, titanium, or aluminum.
The recycling process for your printed items varies with the type of material the item is made from. The two common processes include:
- Shredding, extruding, and melting your old prints into reusable filament (typically used for plastic materials)
- Contacting local recycling centers (especially for metal recycling)
Recycling 3D Printer Materials

Single-use raw materials such as plastic powders used to be commonplace in 3D printing operations in the past. However, the creation of recyclable materials has become a great way to reduce 3D printing waste.
Recycling Powder
Recycling 3D printer powders involves collecting and reusing unused or excess powder from previous prints. This can lead to reduced waste as well as cost savings. However, not all 3D printers can recycle powders and they all require new powder at different frequencies.
Companies looking to improve the sustainability of their 3D printer materials should look towards Nexa3D’s QLS series. These SLS 3D printers allow designers to use end-of-life powder from other SLS and MJF machines to produce high-quality parts–while eliminating powder waste.
For example, companies like JawsTec have been able to save over two tons of powder each year with the aid of Nexa3D printers. Before working with Nexa3D, JawsTec had to forgo usage of 30% of their thermoplastic powder–while also bearing the cost of its storage and disposal in accordance with regulations. This waste of end-of-life powder not only raised the company’s operating overhead and impacted profit, but also represented a significant environmental issue for a company committed to sustainable manufacturing.
By switching to Nexa3D’s QLS 230 and QLS 820 machines, JawsTec now has “zero-waste” SLS 3D printing solution with industry leading powder recyclability rates. The printers can use a combination of new sintering powder and recycled powder from legacy SLS and MJF platforms to produce high-quality parts for their top-tier manufacturing customers. JawsTec can also utilize 100% of their powders due to the high packing density rate of the QLS series printers, which further optimizes the recycled powder usage rates.
Recycling Filaments
Recycling filaments involves reusing waste filaments left over after a 3D printing operation. Manufacturers can choose to reuse filaments from their operations or purchase recycled filaments at affordable prices. Recycled filaments purchased from manufacturers are typically treated to remove impurities and then reprocessed into new usable filament for future prints.
Recycling filaments helps to reduce 3D printing waste as it prevents the disposal of unused or discarded printing materials, thereby minimizing environmental impact. This process promotes a more sustainable approach to 3D printing by utilizing resources efficiently and reducing the overall consumption of virgin materials.
Recycling Resin
While you can’t recycle all resin, some resins can be reused or upcycled. Here are some tips for recycling or reusing resin:
- Grind up cured resin scraps into small pieces before recycling or upcycling. This will make it easier to process and reuse the resin.
- Clean all resin scraps before recycling or upcycling. This will help to prevent contamination of other materials.
- Label all resin scraps with the type of resin they are made from. This will help recycling centers to properly process the resin.
More About 3D Printing Products to Reduce Waste
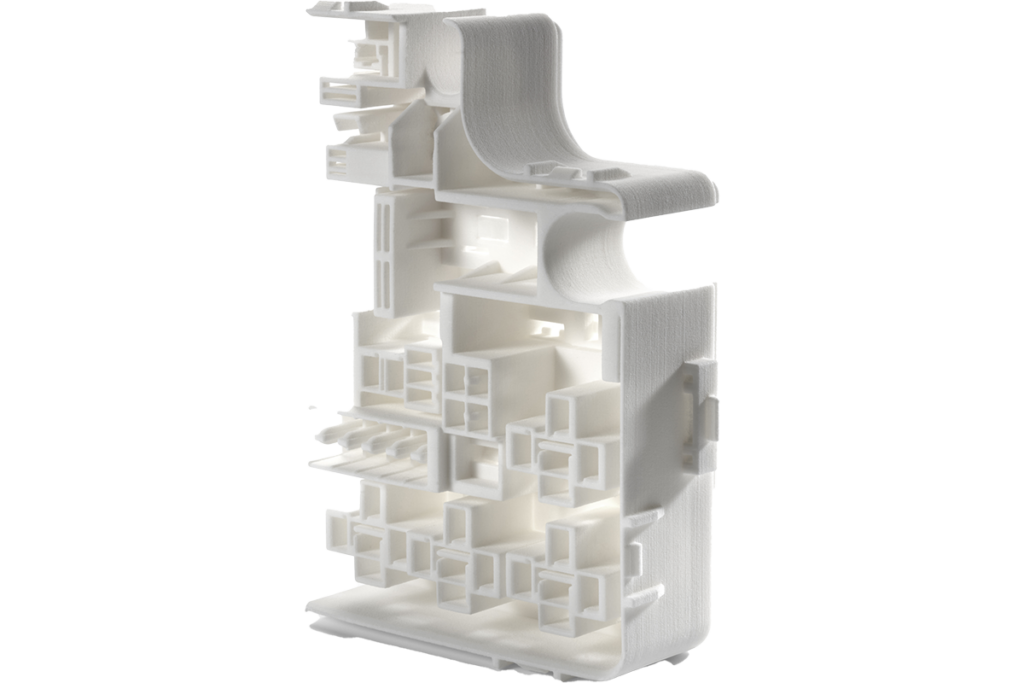
Nexa3D SLS 3D printers can utilized end-of-life materials from a range of suppliers to produce high quality parts while reducing costly waste.
Is 3D Printing Harmful to the Environment?
Compared to many traditional manufacturing processes, 3D printing is generally considered to be less harmful and more beneficial for the environment. Traditional manufacturing often involves large-scale production, which can lead to overproduction, excess waste, and higher energy consumption. In contrast, 3D printing allows for more precise and localized production, reducing the need for transportation and minimizing waste.
Plus, Nexa3D’s line of printers are making it possible to recycle unused powders, ensuring companies can enjoy a sustainable line of production.
Can 3D Printing Reduce the Carbon Footprint of a Product?
Yes, 3D printing reduces the carbon footprint of a product. This can be noted in its ability to lower the carbon emissions associated with shipping and other benefits like on-demand production, production of lightweight parts, and local production.
Use Environmentally Friendly 3D Printers
To reduce waste with 3D printing, it’s essential to prioritize the use of environmentally friendly 3D printers. At Nexa3D, we recognize the significance of sustainability and our commitment is reflected in our printer technology. Our 3D printers utilize an open material platform, allowing you to print with reusable thermoplastic powders and plant-based resins. This reduces material consumption and promotes a circular economy within the 3D printing process.
Additionally, we collaborate with leading material providers to offer a wide range of high-impact functional materials that can be tailored to meet your mechanical requirements and performance needs. This ensures that you can achieve sustainable manufacturing without compromising on quality or functionality.
Join us in embracing sustainable practices for a greener future.
