- Markforged Onyx Filament Review & Alternatives [2024] - December 11, 2024
- 17 Best Professional 3D Printers: Commercial, Desktop, & Industrial [2024] - December 10, 2024
- Best 3D Printers (Industrial, Desktop, & More) [2024 Guide] - July 20, 2024
Short for Stereolithography Apparatus, SLA 3D printing is a vat photopolymerization 3D printing process that fabricates a structure layer by layer. It’s become a popular 3D printing method for manufacturers and engineers due to its ability to create high-resolution, high-quality products.
However, much of the success of SLA 3D printing can depend on what SLA resin you’re using. With so many options available, it can be difficult to determine what type is right for a given product.
This article will review the different types of SLA resins, their benefits, and tips on selecting the right SLA resin for your project.
SLA 3D Printing: An Overview
Stereolithography (SLA) is an additive manufacturing technology that produces objects by selectively curing photopolymer liquid resin through light-activated polymerization. The build platform is lowered into or raised out of a vat of liquid photopolymer resin during the process.
This resin 3D printing process starts with a thin layer of liquid polymer being spread over the build platform. The laser then traces each cross-section of an object onto the surface of the liquid resin, curing it and binding it to the previous layer. The process is repeated from the bottom up until the entire product is built.
SLA 3D printing has come a long way since its inception. The first generation of SLA 3D printing presented challenges including using a single projection point, a slow printing process, and uneven build quality. New resin technologies like Digital Light Processing and Masked Stereolithography have been introduced to address these issues.
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
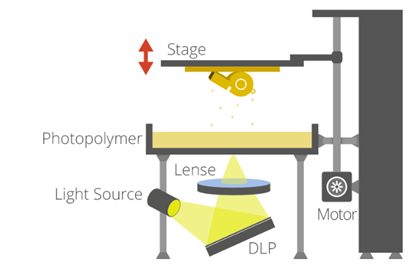
Digital Light Processing is the second generation of resin 3D printing that uses shorter wavelength light to cure resin materials. This technology works with a liquid resin and a projector or an LCD screen to display the images of each layer which then cures when exposed to ultraviolet light.
The projector or LCD screen flashes the image of an entire layer at once, significantly reducing the 3D printing time. This makes DLP a much faster process than SLA and, therefore, more suitable for various applications. However, the light is projected at varying angles, affecting the pixel shape at different spots and making it challenging to produce images with complex geometries and accurate build quality.
Masked Stereolithography (mSLA)
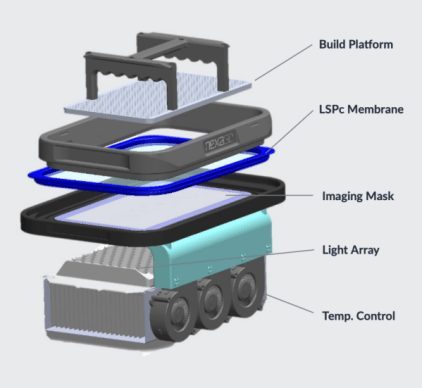
Masked Stereolithography is the latest resin 3D printing technology. It’s an advanced version of SLA that uses an LED array light source rather than a laser or a single projection point.
The LED array projects light through an LCD panel, which masks certain pixels so only specific, unmasked pixels pass through light. Curing occurs only in the unmasked section, and users can get highly-detailed prints faster than traditional SLA and DLP printers while maintaining excellent build quality.
The power of mSLA 3D printing is taken even further with Nexa3D’s proprietary Lubricant Sublayer Photo-curing (LSPc®) technology. LSPc® combines a UV light array with an LSPc Optical lens layer to ensure light uniformity at ultrafast speeds. Its patented lubricated Everlast 2 membrane also significantly reduces the “peel force” imposed as each layer is lifted off of the base of the vat. This allows for the fastest SLA printing on the market at the largest build area in its class–all without sacrificing image quality.
mSLA works with different types of SLA resin materials and is well-suited for various applications. It offers excellent resolution, accuracy, and layer thickness with a wide range of compatible resins like flexible, bio-compatible, and castable resins.
Why Use Resin for SLA 3D Printing?

Smooth Surface Finish
Resin materials offer smoother surface finishes because of their liquid state during printing. Resin 3D printers use a liquid photopolymer resin that solidifies when exposed to light, layer by layer, to create a 3D object.
Also, resin materials often have a higher resolution and can create more intricate designs with sharper edges and finer details. This high resolution capability also allows for better layer heights, meaning that the layers of the 3D printed object can be thinner and more precise. Thinner layers result in a smoother surface finish and better dimensional accuracy, which is particularly important for creating intricate and detailed objects.
High Complexity & Accuracy
Resin materials also allow the user to achieve better accuracy than other 3D printing materials. The layer thickness of resin can be as low as 0.02 mm, which makes it possible to produce parts with intricate details and complex geometries.
Fast Print Speeds
Resin materials allow for some of the fastest 3D printing speeds due to their faster curing time. Resin 3D printing can produce parts in hours, making them ideal for projects requiring quick turnarounds or on-demand production.
Range of Resin Properties
Resin materials offer a wide range of properties that make them suitable for various applications. From flexible and castable resins to bio-compatible and medicinal-grade resins, resin materials are available for almost any use case.
SLA Resin Types (Engineering, Dental, and More)
Various resin types for SLA 3D printing include:
Standard Resin

Standard resin is used in many engineering and manufacturing applications. It is strong and durable yet still lightweight and easy to shape. It can be molded or extruded into various products such as pipes, tubes, furniture pieces, automotive parts, toys, and medical devices.
Properties
- Low viscosity
- Good tensile strength
- Low moisture absorption
Pros
- Lower cost compared to other materials
- Easy to print and finish
Cons
- Reduced heat resistance
- Breaks easily when stressed
Use cases
- Visual models and prototypes
Clear Resin

Clear resin is for products that require transparent parts. It offers the same properties as standard resin but with better optical clarity. The xModel17-Clear is a rigid and durable material with enhanced clarity. This model is great for creating lighting and optics prototypes due to its fine feature detail and smooth surface finish.
Properties
- High optical clarity
- Excellent surface finish
- Fine feature detail
Pros
- It produces highly detailed and transparent parts
- Economical option
Cons
- Prone to discoloration over time
- More brittle and fragile than other resins
Use cases
- Lighting
- Optics prototyping
Durable Resins
Durable resins are a type of SLA resin designed for applications requiring parts with superior durability. x45 is a durable resin that offers excellent mechanical properties while remaining flexible and resistant to wear and tear.
Properties
- Excellent temperature resistance
- Finishes to high optical clarity
Pros
- Draft build mode enables remarkable build speed
- Robust print styles ensure high first-time build success
- Supports a wide variety of modeling and prototyping applications
Cons
- It can be more expensive than other resins
Use cases
- Fast turnaround modeling
- Functional prototypes requiring good strength and toughness
Tough Resin

Tough resin is a type of SLA resin with excellent strength. It’s well-suited for applications that require tough and rigid parts with high-impact resistance, such as in engineering-grade production. The xPP405 is a tough resin that exhibits excellent weathering characteristics and UV stability, making it an ideal choice for design verification models, functional prototypes, and end-use part applications.
Properties
- Good surface finishes
- Excellent dimensional stability
- Exceptionally rigid for a modeling material
Pros
- It has good weathering
- It has a high impact resistance
- Economical
Cons
- It is not recommended for models with thin walls.
- Its print removal may be challenging.
Use cases
- Design verification models.
- Functional prototypes.
- End-use parts, including packaging, piping, and consumer and industrial applications.
Elastomeric Resin
Elastomeric resin is a flexible SLA material with great elasticity. It’s great for parts that require a resilient and flexible finish. The xFlex 402 is an example of an elastomeric resin that offers excellent tear resistance and tensile strength.
Properties
- Firm and soft rubber-like
- Good elongation at break
- Low moisture absorption
Pros
- excellent flexibility
- Average heat deflection
Cons
- Can be brittle if printed too thin
Use cases
- Rubber-like production parts
- Resilience, snap back, and tear resistance elastomeric application
Heat Resistant Resin

Heat resistant resin can withstand temperatures up to 95°C (203°F). This makes them a good fit for parts that require high heat resistance, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries. The xPEEK147 is an example of a heat-resistant SLA resin that offers exceptional dimensional stability and strength at elevated temperatures.
Properties
- High heat deflection temperature
- High stiffness with good dimensional stability
Pros
- Great surface finishes
- Excellent dimensional stability at high temperatures
- Excellent accuracy and aesthetics
Cons
- Can be more expensive than other resins
Use cases
- High-performance prototypes requiring high-temperature capabilities
- End-use parts requiring long-term thermal stability
- Tools and molds requiring good surface and long-term thermal stability above 125°C
Ceramic Resin

Ceramic resin is a type of SLA resin that offers excellent mechanical and chemical properties, meaning it is strong, stiff, and resistant to harsh environments.. It is perfect for applications that require parts with ceramic-like properties, such as prototyping dinnerware or medical equipment and has good tensile modulus at one of the best speeds of any material class. The xCERAMIC 3280 is an example of a ceramic resin providing superior strength and wear resistance.
Properties
- Ceramic look and feel
- High heat deflection
- Smooth black surface finish
Pros
- Excellent rigidity
- High printing speed
- Good weathering
Cons
- It may be more expensive
Use cases
- Wind tunnel methods
- Tooling
- Functional prototypes
Dental Resins
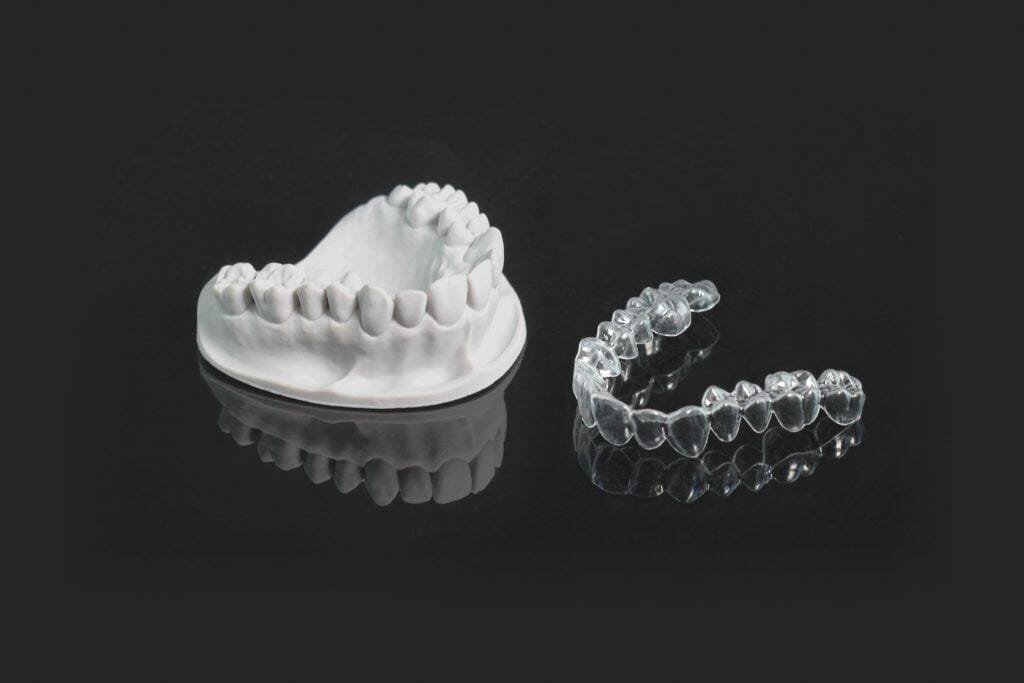
Dental resins are a type of SLA resin with excellent biocompatibility and hardness. This makes it perfect for producing dental parts, such as crowns or bridges. The KeySplint Soft®, KeyGuide®, and KeyModel Ultra™ are all great examples of dental SLA resin that provide excellent printability and dimensional stability.
Properties
- Biocompatibility
- Easy to polish
- Great feature detail
Pros
- High accuracy, resolution, and durability
- Excellent chemical and heat resistance
Cons
- It is best for dental applications
Use cases
- Dental prototypes requiring high detail accuracy
- Splints, night guards and bleaching trays
- Dental thermoforming application
- Dental removal die and model application
More About SLA 3D Printing Materials

What other materials can you use for SLA 3D Printing?
Aside from SLA resin materials, you can use different types of powders for SLA 3D printing. Powder materials are finely ground solid particles that can be used in various industrial processes and applications. They are often made from metals, ceramics, polymers, and composite materials.
What is the best SLA material for prototyping?
Many 3D printers believe SLA resins are best for prototyping due to their superior detail and accuracy. Of course, the best SLA resin will depend on the project requirements. When making parts that require high-impact resistance, such as in engineering-grade production, it is advisable to use a tough resin material.
For instance, Applied Rapid Technologies (ART) utilizes tough engineering grade resin materials like xFLEX, xABS, xCE Black, xPP405, and xPEEK to mold and jig parts on-demand and with superior quality in a fraction of the time it would take to produce them using traditional methods.
Is SLA resin stronger than PLA material?
A 3D printed material’s strength varies by impact resistance, tensile strength, tensile modulus, and tensile elongation. Polylactic acid (PLA) has a tensile strength of around 60MPa, a tensile elongation of about 6%, an impact resistance of about 5 kJ/m2, and a tensile modulus around 3600MPa.
The strength properties of resin varies depending on the type. Resins such as xPEEK147 have an extremely high tensile strength of up to 75MPa. The xCERAMIC3280, by far, has the highest tensile modulus of 9410MPa. The tensile elongation at break of the xFLEX402 is 230%. Resins are ideally used to create high-detail objects (like miniatures) and complex geometry.
Use the Best Resins for SLA 3D Printing
Using high-quality resin materials makes all the difference in SLA 3D printing. Various resin materials are available in the market, but they’re not always compatible with every 3D printer. Using a resin 3D printer that offers an open material platform allows you to use the perfect resin for your product at the price you need.
At Nexa3D, we believe in the power of an abundant material ecosystem–all of our SLA printers offer an open-material platform. We also continue to partner with leading material providers to deliver a comprehensive range of high-impact functional materials that are tailored to your mechanical requirements and performance needs.
The Nexa3D SLA 3D printers also come with Lubricant Sublayer Photo-curing (LSPc®), an advanced mSLA technology that ensures higher quality and smoother surface finishes for resin 3D printing.
Ready to take projects to the next level with SLA 3D printing resins? Request a free sample part.
Want to learn more about SLA 3D printing materials?
