- Formnext Reflections: Catalyzing Innovation, Building the Future of AM Solutions - November 19, 2024
- Best Filament Materials for 3D Printing Flight-Ready Aerospace Parts - August 1, 2024
- 9+ Filament Materials for 3D Printed Fixtures and Jigs - July 21, 2024
Advancing sustainability and recycling waste HP powder in Nexa3D QLS 3D Printers
Among these, 3D printing technology has emerged as a promising solution due to its potential to reduce waste and environmental impact. Not all 3D printing technologies share equally effective capabilities though, and one common form of 3D printing, Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), has garnered significant attention for its versatility and efficiency in various industries. With that in mind, let’s explore the sustainability of SLS technology, with a special focus on recycling old HP powder in Nexa3D QLS 230 or QLS 236 SLS 3D printers, thus reducing waste and promoting a greener approach to additive manufacturing.
QLS 230 SLS 3D Printer

QLS 236 SLS 3D Printer

Comparison to Other Technologies: Leading the Charge
When comparing the sustainability of selective laser sintering with recycled HP powder to the native capabilities of Multi Jet Fusion (MJF), the difference is striking. SLS emerges as the most sustainable polymer 3D printing process available today when powered by Nexa3D’s QLS technology and its high recyclability capabilities. The ability to recycle HP powder and produce high-quality parts positions QLS as a frontrunner in sustainable additive manufacturing.

Ultimate Guide for SLS 3D Printing
When it comes to additive manufacturing for real production, Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) stands out for its widespread use, quality, and performance. But how can you determine if it’s the right choice for your production needs and, if so, which PBF technology do you choose?
Industry Impact: The Dual Benefit
The integration of sustainability practices is mutually beneficial for industries and the environment alike. By adopting eco-friendly technologies like Nexa3D QLS 3D printers and recycling HP powder, businesses can reduce their ecological footprint while recognizing additional revenue streams. This harmonious blend of environmental consciousness and economic viability makes the technology a more realistic choice for higher-volume manufacturing applications.
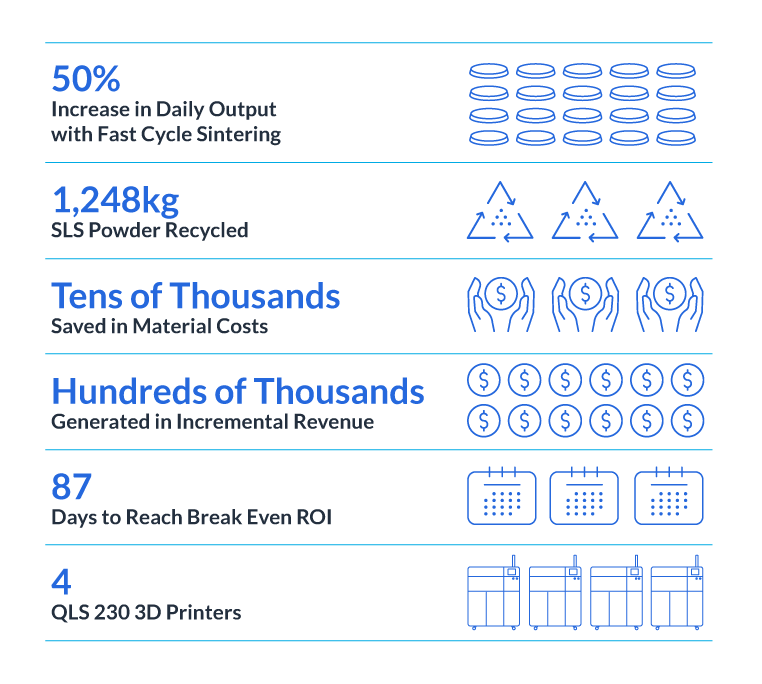
Oscar Klassen from JawsTec expressed how having QLS equipment that turns waste powder into revenue-generating parts has transformed their operations. Previously, they would discard the waste powder, considering it useless. However, with Nexa3D’s technology, they not only reduce their carbon footprint and make sustainable decisions but also generate additional revenue, proving to be a significant win for their business.

Nexa3D’s technology has enabled JawsTec to completely eliminate sintering powder waste. By running a mixture of 75% fresh powder and 25% recycled powder on the QLS 230, they achieve remarkable results. The machine’s enhanced packing density allows them to utilize 100% of the powder across their operations, leaving no room for waste. Additionally, the shorter printing cycles on the QLS platform have raised JawsTec’s SLS manufacturing output by 50%, effectively doubling their productivity.
Recycled HP Materials with Proven Results
- HP PA12 is the most highly utilized thermoplastic across all polymer powder bed fusion technologies. Together with glass-filled PA12, these two plastics make up the majority of all material consumption across SLS and MJF technologies. That is why it’s critical that PA12 powder recyclability has significantly increased with the introduction of QLS technology.
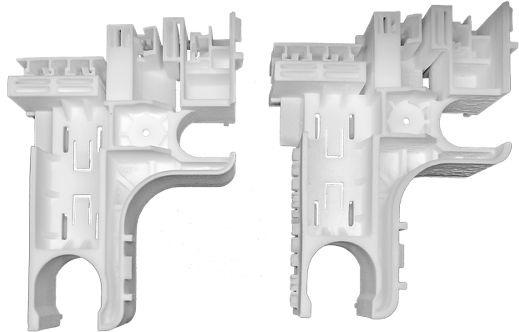
- HP PA12 GB is a glass-bead composite plastic known for its excellent definition and accuracy when printed using SLS technology. However, it often generates a significant waste stream when printing low-density builds on HP machines, often below 8%. By utilizing this waste material in Nexa3D QLS 3D printers, users can convert it into highly usable parts that exhibit tensile strain properties at an impressive 94% of the published technical data for HP PA12 GB. This means that not only is waste reduced, but the recycled parts retain a high level of performance, making them equally viable for various applications.
- HP PA11 is a robust thermoplastic that provides excellent elongation-at-break, impact resistance and ductility along with great chemical resistance. These properties make it a common choice for rugged prototypes and robust end-use production parts. PA11 is also a renewable resource derived from castor beans, making it a strong contender when sustainability is considered, however, its recyclability rates in MJF 3D printers is relatively low. By placing waste PA11 powder from MJF 3D printers into QLS 3D printers, you can manufacture parts that perform to the same standards, while eliminating unnecessary waste.
- HP TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) is a soft and flexible material widely used in medical, consumer goods, and robotic applications. With an advertised shore A rating of 88, it boasts excellent mechanical properties. Traditionally, HP TPU waste generated from Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) technology often tested harder than 90 on the shore A scale. However, the innovative Nexa3D QLS machines have shown the ability to recycle HP TPU waste while maintaining the manufacturer’s specified Shore 88A rating. This capability not only meets the published strength numbers but also reduces the environmental footprint of the manufacturing process.
Extending the Life of HP 580 3D Printers
HP discontinued its HP 580 3D printers in 2022, leading to a challenge for customers who still require these machines. These customers face a substantial waste stream generated by these smaller platforms. However, Nexa3D has offered a sustainable solution by enabling its customers to recycle the waste material from HP 580 3D printers and create bright white PA12 parts on Nexa3D QLS platforms. These recycled parts are ideal for further processing, such as dying and smoothing, adding to their value and potential applications.
The Overall Impact on Sustainability
The sustainability of selective laser sintering technology, particularly through recycling HP powder in Nexa3D QLS 3D printers, marks a significant stride towards a greener future in additive manufacturing. By reusing and repurposing HP powder waste, QLS 3D printers drastically reduce the amount of discarded material, thereby minimizing the environmental impact associated with 3D printing. The ability to retain the mechanical properties of recycled materials ensures that sustainability does not come at the cost of compromised performance. This advancement contributes significantly to a circular economy, where waste is transformed into valuable resources, creating a more sustainable and environmentally responsible approach to manufacturing.
Conclusion
The sustainability of selective laser sintering technology has taken a significant leap forward with the introduction of recycling capabilities in Nexa3D QLS 230 and 236 SLS 3D printers. By repurposing waste materials such as HP TPU and HP PA12 GB, these 3D printers not only reduce environmental impact but also maintain the mechanical properties necessary for diverse applications. Additionally, the ability to recycle waste from discontinued HP 580 3D printers showcases the commitment of Nexa3D to tackle waste challenges responsibly. Real-world user perspectives and industry-specific examples emphasize the dual benefits of reduced waste and increased revenue generation. As this technology continues to gain traction, the collective effort of businesses and manufacturers in embracing sustainable practices paves the way for a more eco-conscious and economically viable manufacturing landscape.
If you are interested in learning more about HP powder recycling with QLS, contact us to discuss how this technology can be used to improve the sustainability of your SLS and MJF operations.

