- Formnext Reflections: Catalyzing Innovation, Building the Future of AM Solutions - November 19, 2024
- Best Filament Materials for 3D Printing Flight-Ready Aerospace Parts - August 1, 2024
- 9+ Filament Materials for 3D Printed Fixtures and Jigs - July 21, 2024
In the realm of 3D printing, innovation is the name of the game, and one of the most exciting recent developments is the implementation of xESD electrostatically dissipative resin. This revolutionary material, paired with Nexa3D printers, is helping electronics manufacturers reduce risks of electrostatic discharge damage on production lines and out in the field for sensitive components.
To delve deeper into the power of printing ESD parts, I caught up with Dr. Olga Ivanova, the Director of Applications & Technology at Mechnano, the leading manufacturer of electrostatically dissipative resin and Nexa3D’s partner for xESD.

Dr. Olga Ivanova is a researcher with more than 10 years of experience in Additive Manufacturing. Her additive manufacturing R&D work includes the Fused Filament Fabrication of textiles to produce military uniforms, developing radiation curable silicones for manufacturing neonatal medical devices, modifying pyrotechnic compositions for decoy flares, allowing them to be 3D printable, and much more.
Q1: What is electrostatically dissipative 3D printing resin, and how does it differ from traditional 3D printing materials?
The key differentiating factor between traditional 3D printing materials and static dissipative materials lies in their electrical properties. Polymers, by nature, are insulators, which means they are unable to conduct electricity. Electrostatically dissipative resins contain a conductive filler that facilitates the gradual dissipation of static charges to the ground, effectively preventing the buildup of static electricity.
Static buildup in insulative parts can pose issues in various applications where the accumulation of static electricity and its abrupt release can be detrimental, causing harm and negatively affecting electronic equipment, mechanical components, and combustible substances.

Q2: What are the key benefits of using electrostatic dissipative 3D printed resins?
Electrostatic dissipative (ESD) resins possess numerous advantages, rendering them highly valuable in industries where the risk of static discharge is a significant concern. Although ESD resins are relatively new, ESD thermoplastics (including filaments and powders) have been utilized for some time. These thermoplastics are used extensively in applications where the occurrence of sparks could lead to catastrophic outcomes, such as in vehicle fuel systems, oil and gas operations, as well as in the manufacturing of microchips and circuits for electronics.
In contrast to ESD filaments and powders, ESD resins demonstrate an exceptional ability to achieve high levels of precision. The XiP Pro offers a resolution that competes with injection molding and precision machining. Moreover, the resulting surface finish is exceptional, intricate part details can be rendered with utmost finesse, and the fabrication speed is faster than traditional manufacturing techniques.

Q3: Are there different types of ESD resin? How does the Mechnano and Nexa3D’s xESD resin stand out in the market?
Yes, there are different types of ESD resins available, but the critical factor that sets them apart from each other is the conductive filler they contain. The more affordable ESD resins in the market commonly incorporate clumped carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Although CNTs possess impressive attributes such as outstanding strength and electrical conductivity, they tend to aggregate or form bundles during the manufacturing process. In this clumped state, CNTs are unable to fully transfer their exceptional properties to the polymer. This results in a performance comparable to carbon black but at a considerably higher cost.
The xESD resin from Mechnano and Nexa3D stands out due to its utilization of functionalized discrete carbon nanotubes (CNTs) that disperse uniformly throughout the resin without aggregating into clumps. This guarantees that every layer of a printed part, irrespective of its build orientation, contains a consistent quantity of CNTs. Known as “D’Func,” this technology not only enables outstanding ESD performance but also enhances mechanical properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and yield strength.
Q4: Are there any specific industries or applications where electrostatic dissipative 3D printed resins are particularly beneficial?
Certainly. The electronics manufacturing industry is a prime example of a sector that significantly benefits from the use of ESD resins. In this field, adherence to ESD standards is crucial. Given the delicate nature of integrated circuits and microchips, even the slightest static discharge can cause severe damage to the part. Consequently, a wide range of precautionary measures are implemented to avoid any introduction of static electricity. These measures encompass the utilization of ESD-compliant shoes, grounded desks, and ionized air.
As the use of these components proliferates across diverse industries, including communications, transportation, defense, space, consumer electronics, and medical devices, there is a growing demand for ESD-compliant parts. Previously, manufacturers had to rely on static-dissipative machined or mold-tooled parts for various applications, which resulted in prolonged lead times and exorbitant costs. xESD resin used in conjunction with the XiP Pro, effectively addresses this challenge by facilitating the rapid production of ESD-compliant parts. This solution proves to be highly advantageous for new product development or short-run production, effectively eliminating the drawbacks of the previous methods.
Q5: Can you provide any tips or advice for users who want to get the best results when 3D printing with Mechnano’s electrostatic dissipative resin? Are there things customers should look for when using a particular ESD resin?
Tip #1: Make sure to review Nexa3D’s Design Guide before starting the part design and build setup. This will help you optimize production speeds and enhance the quality of the parts, ensuring the best possible outcome.
Download the Design Guide for LSPc Printing
When using resin 3D printers (or any 3D printers for that matter) there are several design and prep considerations to ensure that your prints come out successfully every time. This guide focuses on design guidelines for LSPc 3D printing as well as file and print preparations for ultrafast 3D printing.

Download Guide
Tip #2: The inclusion of CNTs in the xESD resin results in an increased viscosity. This elevated viscosity may pose a challenge when removing excess resin from parts with blind holes, hollow chambers, or internal channels during the washing process. In such scenarios, we recommend employing short ultrasonic bath cycles to effectively flush out any trapped resin.
Tip #3: Post-curing of thin, flat parts may lead to deformation or warpage, which is undesirable. Therefore, we strongly suggest incorporating ribbing or constraining the part during the post-curing process.
Tip #4: Discrete and functionalized CNTs integrated into xESD ensure consistent and stable dispersion. It is advisable to exercise caution while using alternative ESD resins, as agglomeration and sedimentation of CNTs may occur within the vat.
Tip #5: If you need support, do not hesitate to contact Nexa3D support. They possess extensive knowledge in using xESD resin, which can help mitigate risks, and they are available to assist in troubleshooting any encountered problems.
Q6: Do you have any examples of users leveraging xESD 3D printing resin?
There are many examples. One case that instantly springs to mind is of a customer who required precise ESD auto-sort pallets to handle fragile crystal resonators. These resonators varied in size, ranging from 8mm x 4mm down to a mere 1.6mm x 1.0mm. The pallets were equipped with 150-400 micro pockets and demanded uniform pocket depths of 80 microns. Notably, the corner hole features on these pallets were so minuscule that they remain imperceptible to the human eye.
The initial attempt by the customer with filament-based systems and more affordable ESD resin on the Formlabs Form3+ and filament options did not yield the desired result. However, switching to xESD resin on the XiP desktop 3D printer produced astonishing results. They were able to replace the expensive and time-consuming machining of ESD pallets in Black Radel, priced at $700 each, with efficient in-house fabrication overnight. This transition significantly reduced their costs and enabled them to iterate on designs to achieve high-quality prototypes for production.
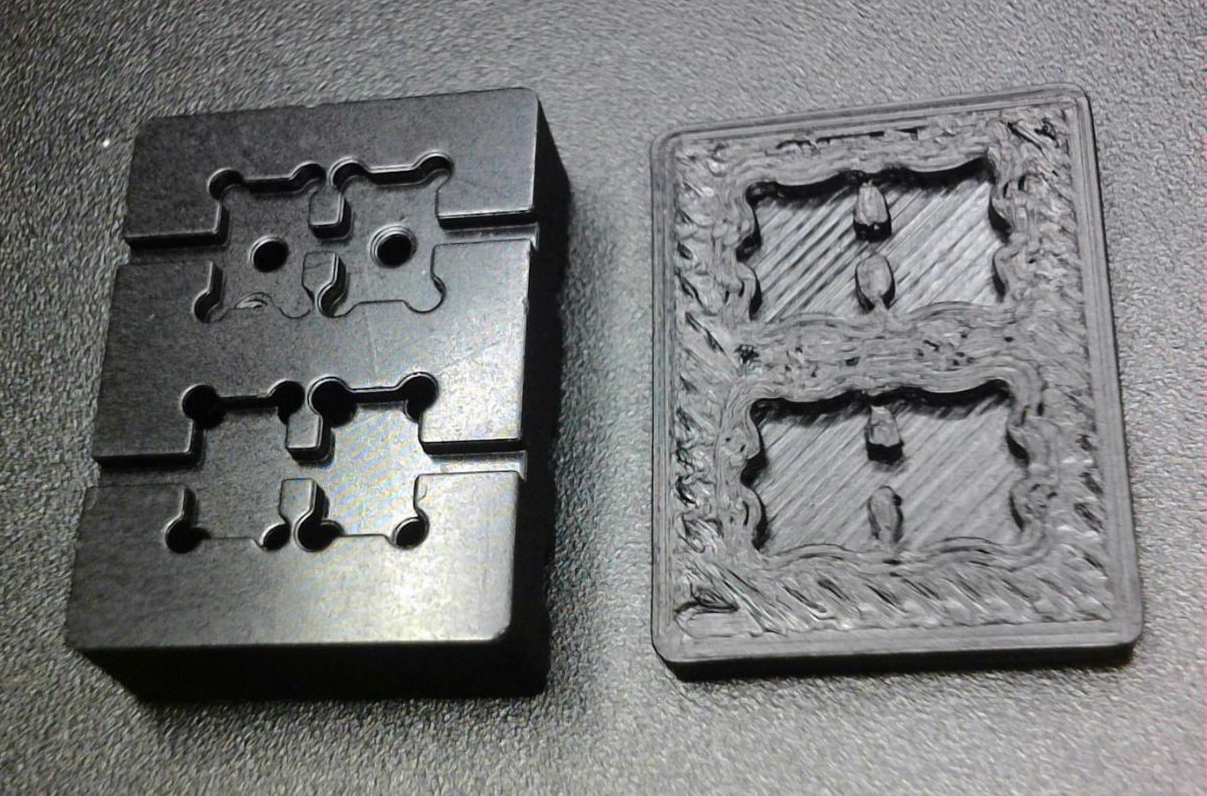
To summarize, xESD resin, alongside XiP and XiP Pro, is transforming the 3D printing landscape. It offers unparalleled electrostatic discharge (ESD) performance, exceptional precision, and rapid production capabilities. Industries such as Electronics Manufacturing are greatly benefiting from this technology, as it enables faster, cost-effective ESD-compliant solutions. The previous example of a customer’s experience serves as a prime illustration of the remarkable potential of xESD resin for high-precision applications. As the world of 3D printing continues to advance, electrostatically dissipative resins are unquestionably at the forefront of innovation.
Contact us today to request a sample part:
